 Goal: Implement strategies that promote Positive Childhood Experiences (PCEs) and reduce the occurrence and impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs).
Goal: Implement strategies that promote Positive Childhood Experiences (PCEs) and reduce the occurrence and impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs).
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events that happen while a person is growing up, and they can have a lasting, negative effect on an individual’s health into adulthood. Examples include experiences such as abuse, neglect, exposure to violence, parental incarceration, divorce, or household issues with mental health or substance use.
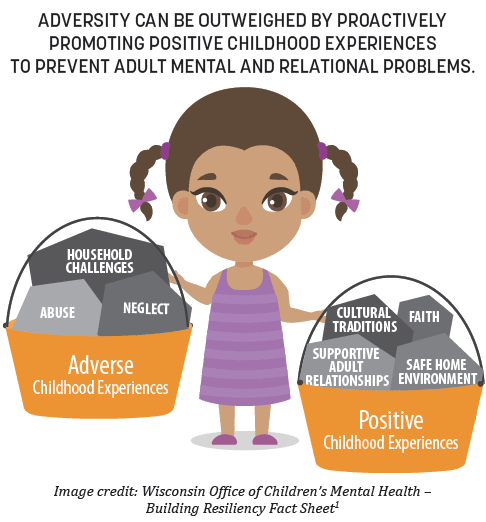 Positive Childhood Experiences (PCEs) are events that can support healthy development. Examples include feeling supported by family and friends, a sense of belonging at school, a positive self-concept, opportunities to have fun, comforting beliefs, and family financial stability.
Positive Childhood Experiences (PCEs) are events that can support healthy development. Examples include feeling supported by family and friends, a sense of belonging at school, a positive self-concept, opportunities to have fun, comforting beliefs, and family financial stability.
Objective: Increase readiness of families, schools, providers, and communities to implement strategies that promote PCEs as a protective buffer to reduce risk associated with ACEs and to improve health outcomes.
Action Steps:
1. Educate shareholders on PCEs and their importance as a protective factor to improve health outcomes.
- Develop opportunities and resources that build understanding of the long-term impacts of ACEs and the compensatory power of PCEs.
2. Encourage partnerships among schools, healthcare and behavioral health providers, and community organizations to offer accessible, culturally responsive, and trauma sensitive programs that build belonging, family resiliency, and supportive communities.
3. Help families navigate and connect to therapeutic services and community programs that relationships and communication skills within the family system.
4. Advocate for policies that support family financial stability.
Financial stress can take a toll on mental health, and economics are one facet of social determinants of health. Rising costs of living and raising a family strain family wellness. Policies that alleviate some of this financial burden like child tax credits, childcare subsidies, and paid parental leave can help families meet their basic needs and reduce the occurrence of ACEs. Programming like Head Start is essential to reduce the harmful effects of poverty and support healthy development of children from low-income families. Policies and programs to support family financial health are needed to reduce ACEs on a mass scale and help youth and parents thrive